|
Process Analytical Technology, PAT - Inorganic
PAT / LIBS / AES / ChemCam / Curiosity / Rover Nd:YAG Laser / Laser Class / SCADA Fertilizer / Iron / Steel / Coal / Bauxites / Alumina / Cement

   
Bio-Technology Raw Materials and Consumables from Taiwan
Knowledge Bases :
I. Process analytical technology (PAT)II. Industrial processesIII. PAT tools
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)
Non-nuclear Radiation free measurement
Atomic emission spectroscopy (AES)
Chemistry and Camera complex (ChemCam)
Curiosity_(rover)
Nd:YAG Laser
Laser Classification
SCADA
Applications :
IV. FertilizerV. Iron and Steel VI. Coal VII. Bauxites & AluminaVIII. Cement
I. Process Analytical Technology, PAT

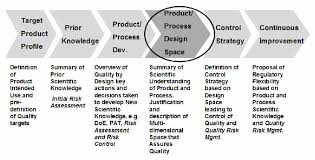
The long-term goals of PAT are to: reduce production cycling time, prevent rejection of batches, enable real time release, increase automation and control, improve energy and material use, facilitate continuous processing.
|
Process analytical technology (PAT) has been defined by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a mechanism to design, analyze, and control pharmaceutical manufacturing processes through the measurement of critical process parameters (CPP) which affect critical
quality attributes (CQA).
The concept actually aims at understanding the processes by defining their CPPs, and accordingly monitoring them in a timely manner (preferably in-line or on-line) and thus being more efficient in testing while at the same time reducing over-processing, enhancing consistency and minimizing rejects.
|
II. Industrial Processes

The long-term goals of PAT are to: reduce production cycling time, prevent rejection of batches, enable real time release, increase automation and control, improve energy and material use, facilitate continuous processing.
|
Industrial processes are
procedures involving chemical, physical, electrical or mechanical steps
to aid in the manufacturing of an item or items, usually carried out on a very large scale. Industrial processes are the key components of heavy industry..
Chemical processes by main basic materialCertain chemical process yield important basic materials for society, e.g., (cement, steel, aluminum,
and fertilizer).
However, these chemical reactions contribute to climate change by
emitting carbon dioxide,
a greenhouse gas,
through chemical reactions, as well as through the combustion of fossil fuels to
generate the high temperatures needed to reach the activation energies of
the chemical reactions.
|
III. PAT tools

Fundamental to process analytical technology (PAT) initiatives are the basics of multivariate
analysis (MVDA)
and design of experiments (DoE).
This is because analysis of the process data is a key to understand the process and keep it under multivariate statistical control.
|
PAT tools
In order to implement a successful PAT project, a combination of three main PAT tools is essential:
- Multivariate data acquisition and data analysis tools: usually advanced software packages which aid in design of experiments, collection of raw data and statistically analyzing this data in order to determine what parameters are CPP.
- Process analytical chemistry (PAC) tools: in-line and on-line analytical instruments used to measure those parameters that have been defined as CPP. These include mainly near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS); but also include biosensors, Raman spectroscopy, fiber
optics and others.
- Continuous improvement and/or knowledge management tools: paper systems or software packages which accumulate Quality Control data acquired over time for specific processes with the aim of defining process weaknesses and implementing and monitoring process improvement initiatives. These products may be the same or separated from the statistical analysis tools above.
|

Schematic of a LIBS system -
Courtesy of US Army Research Laboratory
|
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)
is a type of atomic emission spectroscopy which
uses a highly energetic laser pulse
as the excitation source.The laser is focused to form a plasma, which atomizes and excites samples. The formation of the plasma only begins when the focused laser achieves a certain threshold for optical breakdown, which generally depends on the environment and the target material.LIBS is one of several analytical techniques that can be deployed in the field as opposed to pure laboratory techniques e.g. spark OES.
As of 2015, recent research on LIBS focuses on compact and (man-)portable systems. Some industrial applications of LIBS include the detection of material mix-ups, analysis
of inclusions in steel, analysis of slags in secondary metallurgy, analysis
of combustion processes, and
high-speed identification of scrap pieces for material-specific recycling tasks. Armed with data analysis techniques, this technique is being extended to pharmaceutical samples.
|

LIBS has no No gamma-ray, neutron or X-ray radiation.
|
Radiation exposure is a measure of the ionization of air due to ionizing radiation from photons; that is, gamma rays and X-rays.[1] It
is defined as the electric charge freed by such radiation in a specified volume of air divided by the mass of that air.
The SI unit of exposure is the coulomb per kilogram (C/kg), which has largely replaced the roentgen (R).[2] One
roentgen equals 0.000258 C/kg; an exposure of one coulomb per kilogram is equivalent to 3876 roentgens.
LIBS is Environmentally and personal safe technology No gamma-ray, neutron or X-ray radiation. No governmental permissions and licenses are needed for operating and transporting the equipment making it simpler and cheaper to manage the production.
|

The internal spectrometer (left) and the laser telescope (right) for the mast
|
Chemistry and Camera complex (ChemCam)
is a suite of remote sensing instruments on Mars for
the Curiosity rover.
As the name implies, ChemCam is actually two different instruments combined as one: a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)
and a Remote Micro Imager (RMI) telescope. The purpose of the LIBS instrument is to provide elemental compositions of rock and soil, while the RMI will give ChemCam scientists high-resolution images of the sampling areas of the rocks and soil that LIBS targets.[1] The
LIBS instrument can target a rock or soil sample from up to 7 m (23 ft) away, vaporizing a small amount of it with about 30 5-nanosecond pulses from a 1067 nm infrared laser
and then observing the spectrum of the light emitted by the vaporized rock.
|

Warning label for class 2 and higher
|
Lasers have been classified by wavelength and power into
four classes and a few subclasses since the early 1970s. The classifications categorize lasers according to their ability to produce damage in exposed people, from class 1 (no hazard during normal use) to class 4 (severe hazard for eyes and skin).A Class 1 laser is safe under all conditions of normal use. This means the maximum permissible exposure (MPE) cannot be exceeded when viewing a laser with the naked eye or with the aid of typical magnifying optics (e.g. telescope or microscope).
|
IV. Fertilizer
V. Iron and Steel
VI. Coal

Coal is mostly carbon with
variable amounts of other elements,
chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen,
and nitrogen. |
Calorific value
Ash content
Moisture
Volatiles matter
Carbon
Minerals
Si, Al, Fe, Ti, S, K, P, Na, Ca, Mg |
VII. Bauxites & Alumina

The global production of aluminium in 2016 was 58.8 million metric tons. It exceeded that of any other metal except iron (1,231 million
metric tons)..
|
Bauxite, Alumina, Lime,
CausticNa, Mg, Si, S, Cl,
K, Ca, FeLoss on ignition (LOI)SiO2, Fe2O3, Na2O, CaOTiO2, V2O5, P2O5, Ga2O3
Alloy, Ti, V, Mo, C, Si, Mn, Cr, Ni, CuAsh
|
VIII. Cement

Modern cements are often Portland
cement or
Portland cement blends, but industry also uses other cements.
|
Flux, SinterSiO2, Gypsum Flyash, CaO, Al2O3, Fe2O3Limestone, Slag, Fe total, MgO,
Ca, Si, Fe, Al, Mg, NaMoisture LSF |
Key Words : #PAT #LIBS #Radiation #AES #ChemCam #CuriosityRover#Nd #YAG #Laser #SCADA#Fertilizer #Iron #Steel #Coal #Bauxite #Alumina #Cement
|